What are recurrent payments?
Recurring payments are transactions that customers pre-authorise to occur automatically at regular intervals, such as weekly, monthly, or annually.
They often relate to subscription services, memberships, utilities, or instalment plans.
Recurrent payment identification centres around four factors:
-
Enriched transaction data,
-
Flexible payment authorisation methods, such as VRP,
-
AI-driven pattern detection, and
-
Deep integration with customer management platforms.
Their main aim is to deliver greater accuracy, control, and transparency in managing automated payments.
Did you know?
The subscription payment market is projected to reach $1.5 trillion to $1.94 trillion by 2033 and 2035, meaning it will more than triple in size compared to the current $ 557.8 billion.
Furthermore, the relatively higher CAGR of approximately 9.5% from 2025 to 2029 in subscription billing management reflects intensified demand for automated billing and payment infrastructure.
4 key factors for identifying recurrent payments
The above factors have greatly impacted how businesses, banks, and consumers identify, track, and control recurring charges.
1. Advanced data enrichment
Advanced data enrichment in payment processing and transaction records has improved the identification and management of recurrent payments by embedding rich metadata and contextual details far beyond basic transaction information.
Data enrichment transforms raw payment transaction data, often cryptic codes and inconsistent merchant names, into structured, clear, and actionable information.
For example, instead of seeing ‘POS DEBIT 0421,’ enriched data shows ‘Starbucks Coffee – Coffee & Snacks’ with additional context such as merchant category, location, and even customer behaviour signals.
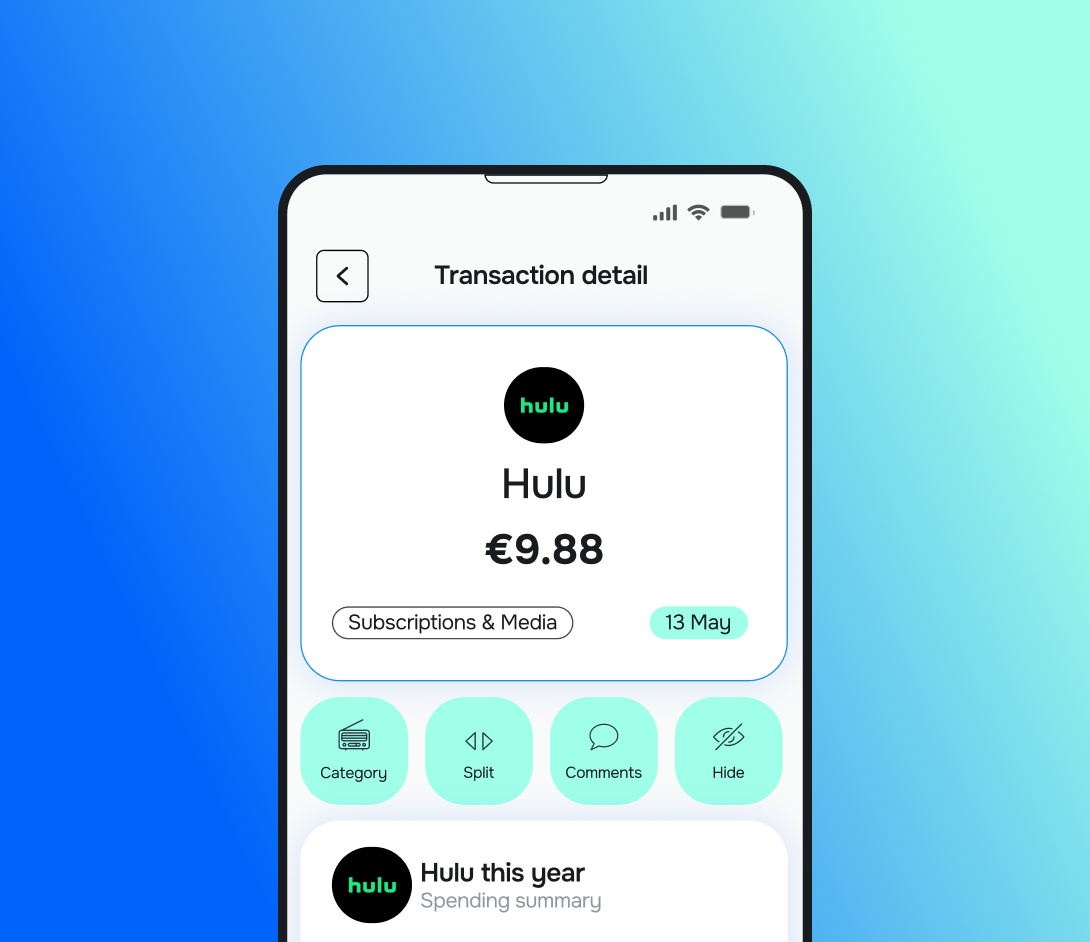
Modern payment processors and banks embed key details into transaction records that allow precise identification of recurrent payments:
-
Merchant identity and category: Clear vendor names and standardised Merchant Category Codes (MCC) classify merchant types such as subscription services, utilities, or retailers.
-
Payment plan type: Distinguishing fixed subscriptions, tiered pricing, usage-based billing, or one-time purchases.
-
Billing frequency and next billing date: Clarifies whether a transaction is billed monthly, quarterly, or annually and anticipates future charges.
-
Contract and subscription ID: Links each transaction to specific customer agreements.
-
Auto-renewal notifications: Indicates whether payments will be renewed automatically or require customer action.
As a result, this enriched data enables banks, fintech apps, and merchants to:
-
Accurately detect and classify recurring transactions, separating them from one-offs or refunds.
-
Provide customers with clear and understandable descriptions of charges, reducing confusion and disputes.
-
Proactively notify customers of upcoming payments or price changes using enriched insights.
-
Automate reconciliation and reporting with consistent transaction categorisation.
-
Support new payment models such as Variable Recurring Payments (VRP) enabled by open banking APIs.
How can Meniga help extract value from transaction data?
By aggregating, consolidating, and enriching both internal and open banking data, we help organisations gain a comprehensive, 360-degree view of their customers’ spending patterns and overall financial behaviour, supporting better decisions and more relevant services.
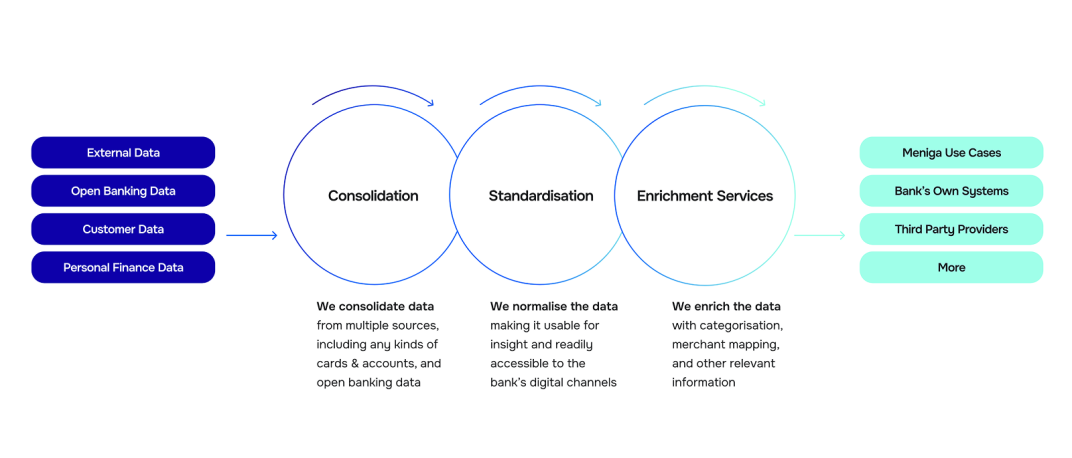
Our Enrichment Engine turns raw transaction data into a meaningful, visual story of your customers’ financial lives.
Powered by machine learning, the system becomes even more precise over time, continuously improving through user feedback and community input.
2. Variable Recurring Payments (VRP)
Enabled by open banking APIs, VRPs let customers authorise payments that recur on a schedule but can vary in amount directly from their bank accounts.
They provide substantial benefits over traditional fixed-amount recurring payments, such as direct debits or card-on-file transactions.
Because each VRP is linked to a bank-authenticated mandate, both merchants and consumers gain real-time visibility into payment schedules and amounts.
This flexibility offers greater control and transparency in managing ongoing payments.
Payments are processed instantly, with clear visibility of amounts and schedules, ensuring customers know exactly when funds are withdrawn from their accounts, improving financial management.
In addition, VRPs eliminate the need for sharing sensitive card details with merchants, as payments are authorised and processed through the customer’s bank, reducing the risk of fraud.
The most common uses of VRP include:
-
Utility and energy bill payments based on actual usage.
-
Subscription payments with variable fees or flexible plans.
-
Government payments such as taxes, fees, or benefits.
-
Financial services repayments, such as mortgages or loans, with varying instalments.
-
Ecommerce transactions with one-click checkout convenience without card-on-file risks.
3. AI and machine learning
They analyse vast amounts of transaction data to detect recurring payment patterns, even when amounts or intervals fluctuate.
As a result, this is significantly improving classification accuracy and operational efficiency.
Smarter pattern recognition
Modern AI algorithms go far beyond simple schedule matching. They consider multiple layers of information, such as Merchant Category Codes (MCC), payment device fingerprints, customer profiles, and historical behaviours.
This multi-dimensional approach uncovers subtle recurring patterns, including variable amounts or irregular intervals, enabling more accurate differentiation between genuine recurring payments, one-off transactions, and potential anomalies.
Proactive customer engagement
Machine learning models can now anticipate payment issues before they occur.
By analysing user behaviour and historical data, they predict potential failures and trigger timely interventions, from reminders and alternative payment suggestions to dynamic retry scheduling.
This proactive approach reduces involuntary churn and improves customer satisfaction by addressing issues before they impact the user experience.
Personalisation and optimisation
AI-driven personalisation tailors communication and recovery strategies to different customer segments, improving engagement and response rates.
It also optimises key operational decisions in real time, such as the ideal payment method, transaction timing, or routing network to boost success rates and reduce processing costs.
According to the words of Anna Skibicka, our Senior Product Manager for the Meniga Insight Platform: ‘Why settle for simple segments and push notifications when today’s technology can offer so much more?
With Meniga Insights, banks can consolidate data beyond transactions to build rich 360° user profiles.
They can:
-
Evaluate numerous labels and eligibility checks in real-time, allowing for dynamic segmentation.
-
Assign different content variants depending on the behavioural traits of the user receiving the insight, or based on how they currently interact with their banking app.
This allows banks to leverage ongoing or predicted trends and behaviour to act on opportunities instantly.
This way, no two banking customers will have the same banking experience. This is the essence of true hyper-personalisation.’
For more useful insights about AI and personalisation, read the main takeaways from our 2025 Meniga Customer Conference, held in September.
Enhanced fraud detection and security
AI continuously monitors transactions for irregularities, using behavioural analysis and real-time data to detect suspicious activity.
Unlike static, rule-based systems, AI models evolve alongside emerging threats, offering adaptive and robust protection for both merchants and customers.
4. Integration with customer systems
The integration of recurrent payment identification and management with customer systems, such as CRM, ERP, and subscription management platforms, is necessary for efficient and accurate payment handling.
Cross-referencing agreements and contracts
Integration enables real-time linkage of payment transactions to customer agreements and contracts stored in CRM and ERP systems.
This ensures that payments align with agreed-upon subscription terms, billing frequencies, and contract conditions, thereby reducing errors and disputes.
For example, if a payment schedule changes or a subscription is cancelled, the systems automatically sync to reflect those updates in billing and collections.
Improved payment recognition and automation
By combining payment data with customer lifecycle information from CRM and ERP systems, platforms can more accurately identify recurring transactions linked to active contracts, distinguishing them from one-time transactions or refunds.
As a result, this minimises false positives or missed recurring payments.
Automation through integrated systems streamlines renewals, upgrades, downgrades, and cancellations, eliminating the need for manual intervention and ensuring billing accuracy, while also improving customer experiences.
Dispute reduction and reconciliation
Integrated data flows enable finance teams to efficiently reconcile payments with contracts and invoices, reducing the administrative burden and the likelihood of disputes.
When a payment anomaly occurs, customer service can quickly access the relevant contract history and resolve the issue promptly, thereby boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Automated notifications and renewals
The integration supports automated customer notifications for upcoming renewals, payment reminders, failed payments, or subscription changes directly from CRM or subscription management tools.
Personalisation of communications is enhanced by using customer profiles and segmentation data from CRM systems to reduce churn and improve retention.
Enhanced reporting and forecasting
Unified data from payments, customer relationships, and operational systems enables comprehensive reporting and accurate revenue forecasting.
Thus, you can gain insights into subscription trends, customer lifetime value, and financial health, driving better strategic decisions.
How to minimise failed recurring payments: 8 best practices
Adopting smarter, data-driven strategies can improve recovery rates and reduce involuntary churn. Here are the most effective approaches.
1. Implement smart retry logic
Use intelligent retry systems that adapt based on the reason for the payment failure, such as insufficient funds or technical errors.
Data-driven scheduling can optimise retry timing and gradually reduce the frequency of attempts, balancing recovery efforts with a positive customer experience.
2. Enhance customer communication
Send reminders before recurring charges and immediate notifications if a payment fails, clearly explaining the issue and how to resolve it.
You can leverage multiple channels, including email, SMS, and in-app messaging, to ensure customers receive and act on these updates quickly.
3. Offer multiple payment methods
Providing a range of payment options, from credit and debit cards to digital wallets, ACH, and Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) solutions, increases the likelihood of successful transactions. Offering alternatives also suits diverse customer preferences and reduces the impact of a single payment method failing.
4. Leverage account updater services
Reduce declines caused by expired or replaced cards by using account updater services offered by card networks.
These services automatically refresh payment credentials, keeping subscriptions active without requiring customer intervention.
5. Simplify the payment experience
Make it easy for customers to complete or update payments.
Use real-time validation, autofill features, and saved payment details to minimise input errors.
Ensure that updating billing information is quick and smooth, with as few steps as possible.
6. Automate and personalise dunning sequences
Automated dunning workflows, featuring scheduled notifications and retry attempts, help recover missed payments efficiently.
Adding personalisation, such as tailored messaging based on customer value or payment history, improves response rates.
7. Monitor and analyse payment data
Continuously track key metrics such as failed payment rates, recovery success, churn, and customer lifetime value.
Use these insights to refine retry strategies, communication timing, and messaging. In addition, segmenting customers by profile or value can further enhance recovery efforts.
8. Strengthen fraud prevention and compliance
Implement robust fraud detection tools and adhere to industry standards, such as PCI DSS, to minimise declines triggered by security concerns.
Strong security practices protect customer data, build trust, and reduce false declines.
How can you optimise the recurrent payment process with Meniga?
Meniga is a digital banking solution provider that relies on its advanced data enrichment, analytics, and customer engagement capabilities to deliver transparency, automation, and intelligent engagement.
With Meniga, you can:
1. Identify, track, and analyse subscriptions to help customers understand and optimise their recurrent spending.
2. Display clean and accurate merchant names for an accurate overview and improved search.
3. Assign current logos for easy identification and visualisation.
4. Provide a localised and language-specific website address based on transaction data.
5. Analyse behavioural data to create ultra-specific customer segments, such as Likely to Invest or Starting a Family.
6. Leverage real-time events from any external or internal banking tool to ensure timely delivery.
7. Alert customers to upcoming charges or potential payment failures and suggest corrective actions.
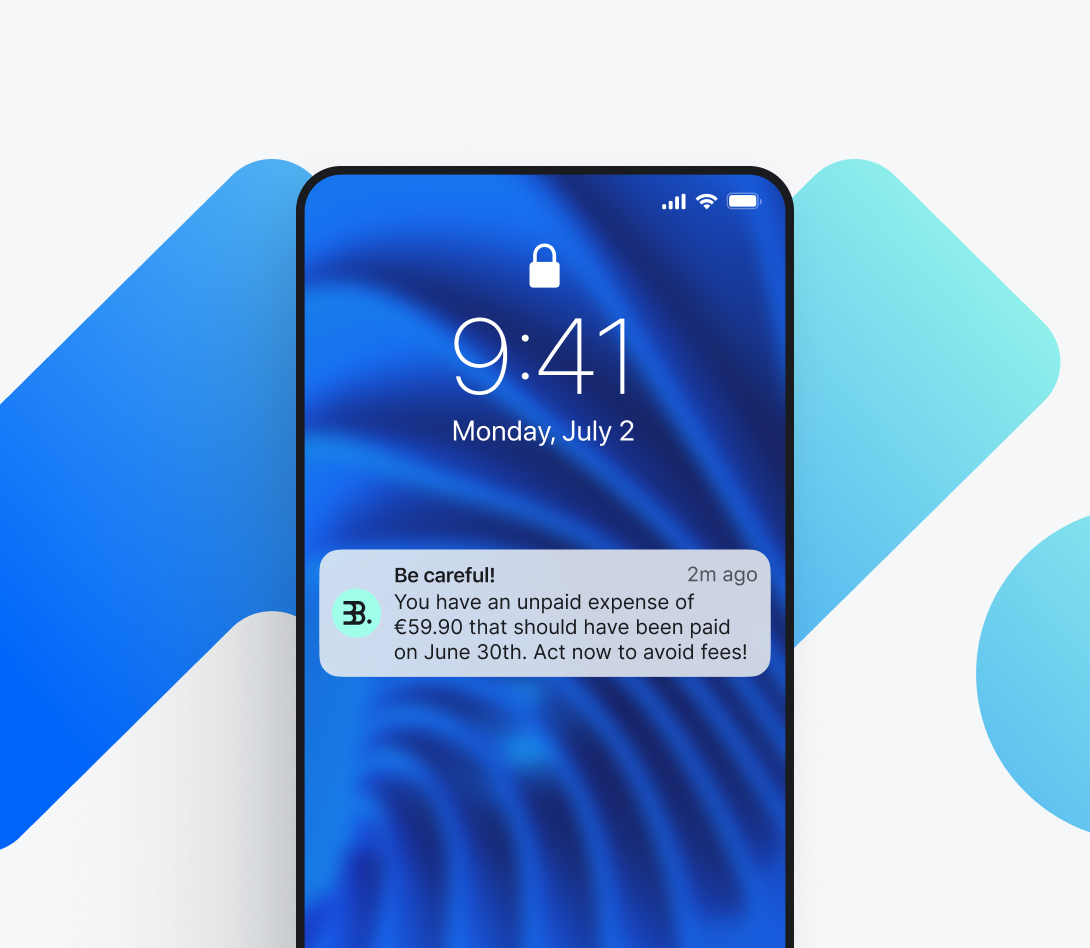
8. Provide tailored financial guidance to optimise customers' budgets, contributing to improved financial literacy and confidence over recurring commitments.
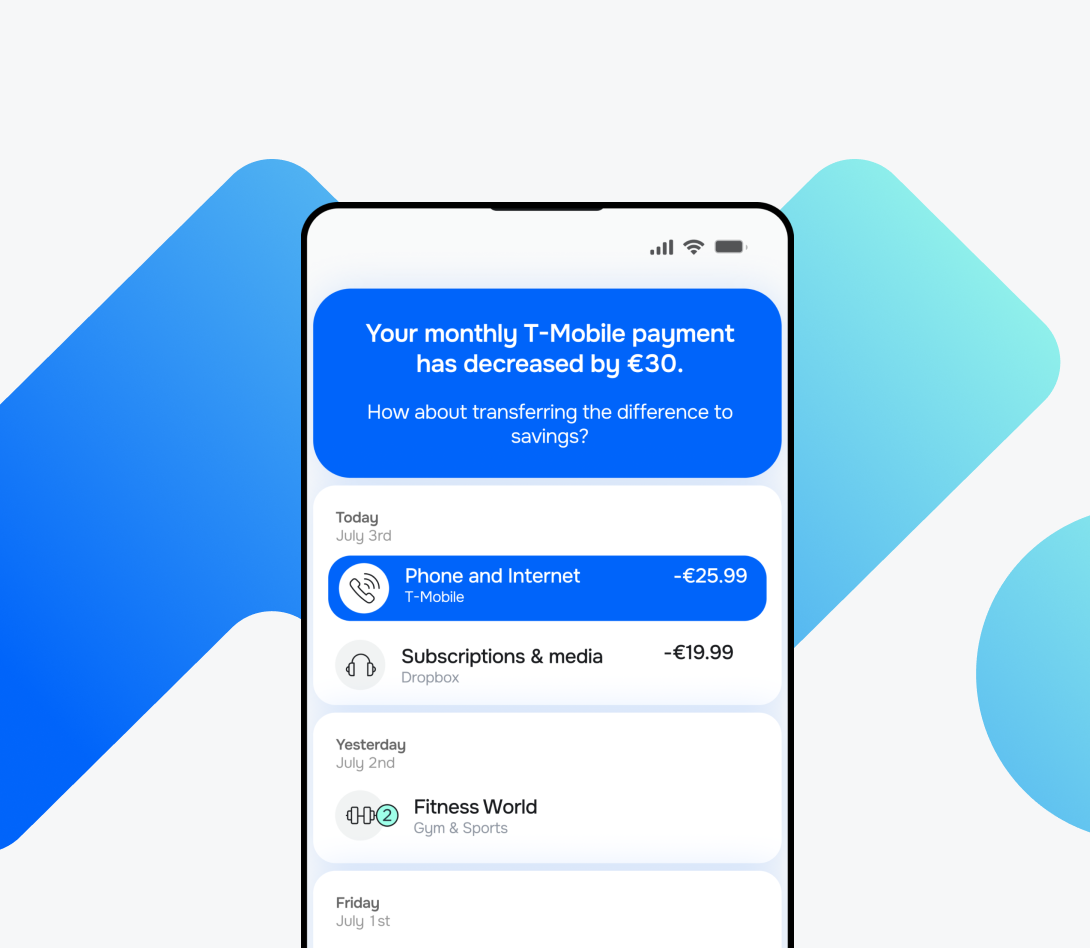
Enticed to learn more?
Contact us today to unlock the full value of your transaction data to drive growth, retention and customer satisfaction.








