Recurring payments are at the core of banking, but managing them has become increasingly complex.
Failed renewals, false declines, and growing subscription volumes are affecting margins while fintechs set new standards for smooth experiences.
And as customers expect frictionless automation, traditional systems struggle to keep up.
AI-powered recurring payment management is helping banks make recurring payments more efficient and strategic.
Read on to see how you can leverage AI-powered recurring payment management to drive more loyalty and growth.
What does recurring payments management involve?
Recurring payment management is the automated handling of scheduled payments that customers authorise, from subscriptions and utility bills to loan repayments and memberships, deducted from their accounts at agreed intervals.
Recurring payment systems oversee the entire lifecycle of these transactions:
-
Capturing customer consent,
-
Securely storing payment data,
-
Scheduling payments, and
-
Processing them automatically without manual intervention.
It involves strict compliance with data security standards, such as PCI DSS, advanced tokenisation to protect sensitive details, and coordination with payment gateways and processors to do transactions in a reliable way.
Benefits for banks are clear. Automated recurring payments mean predictable cash flow, higher customer retention, and greater satisfaction due to the convenience of uninterrupted services.
AI, behavioural nudging, and smarter savings: 3 key strategies for recurring payments management
Recurring payments management:
-
Leverages AI for optimization and fraud prevention,
-
Adopts VRPs for flexibility, and
-
Uses behavioural nudging to encourage smarter saving.
They all contribute to a more efficient, adaptable, and customer-friendly payments ecosystem.
1. The role of AI-driven recurring payments management
AI influences how banks optimise recurring payments, bringing smarter automation, predictive insights, and personalised customer engagement across the entire payment lifecycle.
A key advancement lies in how AI manages failed transactions. In the past, payment retries followed a static approach that often led to repeated failures.
Nowadays, however, AI-driven systems analyse each transaction in real time, relying on details such as the issuer, merchant category, time of day, and historical payment behaviour to determine the most effective retry timing and method.
It results in higher recovery rates, lower churn, and a better experience for both banks and customers.
| How AI enhances customer engagement in subscription billing |
| Aspect | AI contribution | Benefit |
| Proactive interactions | AI analyses payment history, usage patterns, and behaviour to identify at-risk customers and predict churn early | Enables timely intervention with tailored offers and flexible payment options |
| Personalised communication | Segments customers based on preferences, engagement, and subscription history to deliver targeted reminders and discounts | Increases customers feeling valued and understood, reducing churn |
| Billing and revenue automation | Automates billing, invoicing, and dynamic pricing adjustments based on market demand and customer behaviour | Ensures consistent, error-free billing and value-aligned offers |
| Customer support | AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 instant support for common queries, freeing human agents for complex issues | Enhances responsiveness and overall user satisfaction |
| Engagement transformation | Converts subscription billing from a transactional process into an intelligent engagement platform | Drives customer retention, maximizes lifetime value, and fosters long-term relationships |
Another aspect that AI is also influencing is predictive analytics.
1.1. AI-predictive analytics
AI-powered predictive analytics is giving banks the ability to see and act ahead of payment problems.
By forecasting potential payment failures and churn risks before they happen, banks can proactively reach out to at-risk customers with timely, tailored messages or alternative payment options.
As a result, it leads to stronger retention and higher customer satisfaction.
AI also personalises how and where customers are engaged, from choosing the right communication channel to crafting message content that resonates with individual preferences.
When payments do fail, this level of personalisation significantly improves recovery and resolution rates.
Meanwhile, real-time analytics provide deep visibility into payment behaviour, enabling banks to continuously fine-tune retry strategies and billing cycles.
Besides stabilizing cash flow it also drives sustainable revenue growth through smarter, data-driven decision-making.
How can Meniga help with delivering timely and personal messages?
Meniga Insights enables banks to move beyond basic transaction data, creating a truly comprehensive 360° view of each customer.
With this deeper understanding, banks can achieve smarter segmentation and more relevant engagement.
Using real-time analytics, banks can evaluate multiple data points and eligibility criteria instantly, enabling dynamic segmentation that adapts as customer behaviour changes.
Content and recommendations can then be tailored to match each user’s unique behavioural traits or interaction patterns within the banking app ensuring every message feels timely and personal.
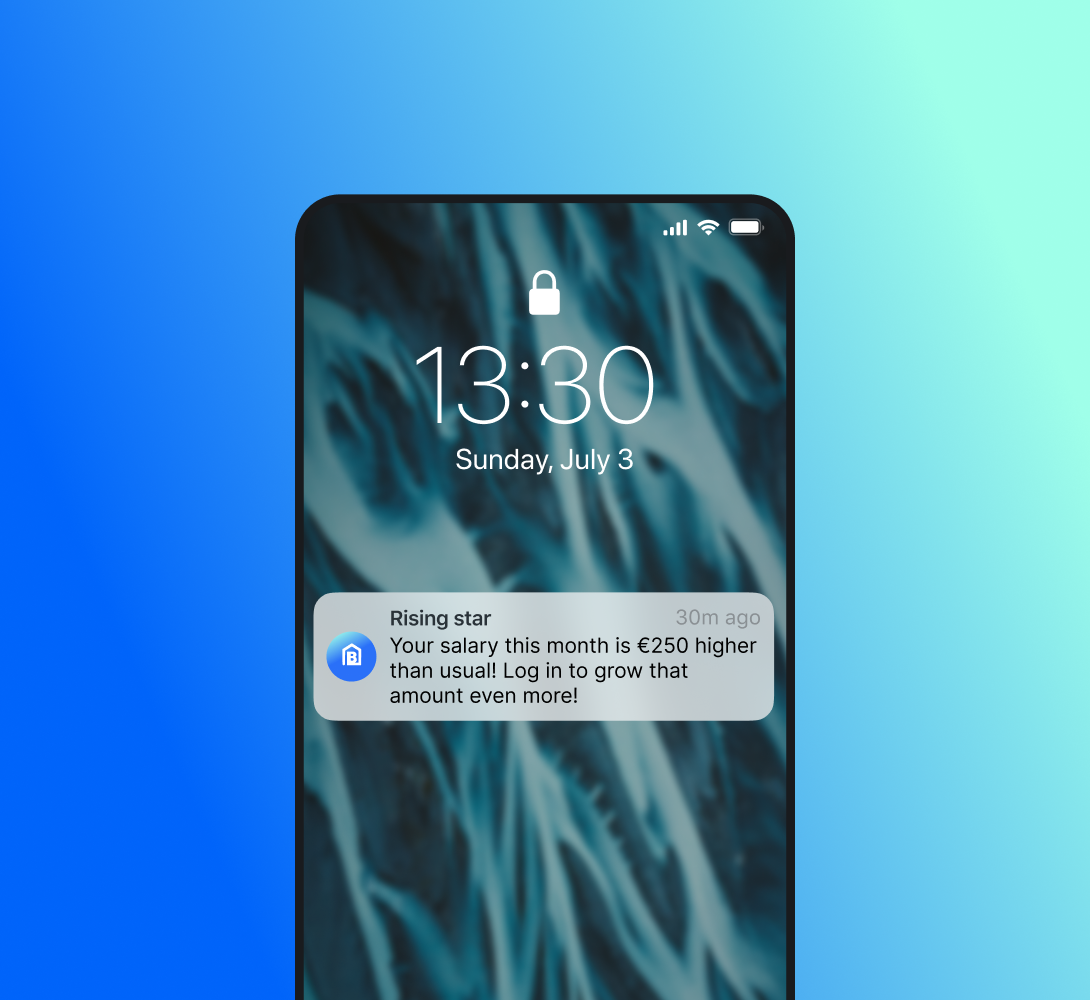
By analysing both current and predicted customer trends, banks can respond to opportunities the moment they arise , turning insight into meaningful action that drives stronger relationships and better results.
2. The role of behavioural nudges in recurring payments management
Behavioural nudges are a powerful tool in recurring payments, subtly shaping customer actions to encourage on-time payments, reduce failures, and promote better financial habits.
Rather than enforcing strict rules, nudges work through gentle psychological prompts grounded in behavioural economics, which guide customers toward choices in their own best interest.
Banks use personalised nudges such as:
-
Timely reminders before payment due dates.
-
Motivational prompts that reinforce positive behaviour.
-
Social proof cues like '85% of customers pay on time’ that normalize responsible payment behaviour.
-
Framing messages around loss aversion, for example, 'Pay now to avoid late fees.'
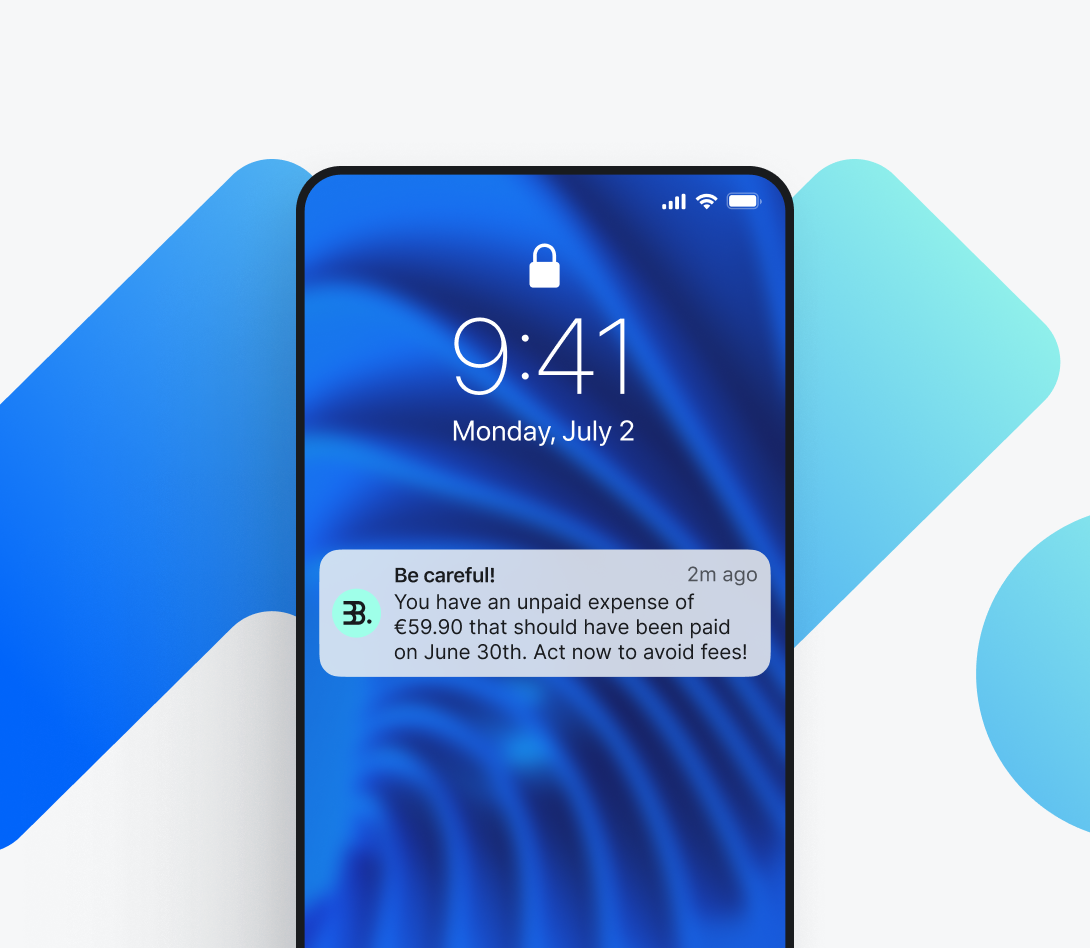
These strategies rely on natural cognitive biases like present bias and loss aversion, making customers more likely to act promptly.
Powered by AI-driven analytics, banks can now tailor these nudges in real time to match individual payment patterns and cash flow trends, turning behavioural insights into measurable improvements in payment reliability and customer satisfaction.
However, you shouldn’t overlook the importance of ‘calibrating’ nudges carefully, as overly aggressive or poorly timed nudges can cause financial stress or distrust among customers.
The best nudging strategies balance encouragement with users’ liquidity needs, helping with better financial habits and healthier cash flow management without causing over-saving or pressure.
| Ethical nudges | Manipulative nudges |
| Transparent Intent: Clearly disclose the nudge purpose and allow opt-out options. For example, savings apps that transparently suggest setting aside small amounts without hidden motives. | Hidden motives: Nudges that disguise upselling or fees, such as automatically enrolling users in paid services without clear consent. |
| Preserves autonomy: Allows freedom of choice and respects decisions, such as easy cancellation of subscriptions or opting out of additional services . | Coercive Design: Difficult cancellation or account closure processes, trapping customers into unwanted services. |
| Promotes well-being: Aims to improve financial health and send reminders for timely payments to avoid fees or nudges encouraging sustainable saving behaviour. | Exploits biases: Uses fear-based tactics like FOMO or guilt to push quick purchases or investments. |
| Fairness and non-discrimination: Designs nudges free from algorithmic bias, ensuring equitable treatment across user groups. | Algorithmic bias: Nudges trained on biased data that disadvantage vulnerable populations or increase inequalities. |
| Enhances trust: Builds user confidence by providing clear, honest information and respecting privacy, avoiding dark patterns. | Deceptive UI: Misleading interfaces or disguised ads that trick users into unwanted actions or data sharing. |
3. The role of smart savings in recurring payments management
Smart savings go beyond simple round-ups and fixed deposits.
They help customers manage liquidity, prevent payment failures, and achieve long-term financial wellness.
Banks leverage machine learning and behavioural analytics to:
-
Understand individual spending patterns,
-
Predict upcoming expenses, and
-
Automatically set aside just the right amount at the right time.
This proactive approach ensures customers always have enough funds available for recurring payments, reducing failed transactions and overdraft incidents while promoting healthy financial habits.
For example, AI-driven systems can dynamically adjust savings contributions based on cash flow trends, income variability, and spending behaviour.
When a customer’s expenses increase, the system scales back automated savings.
On the other hand, when surplus funds appear, it increases contributions.
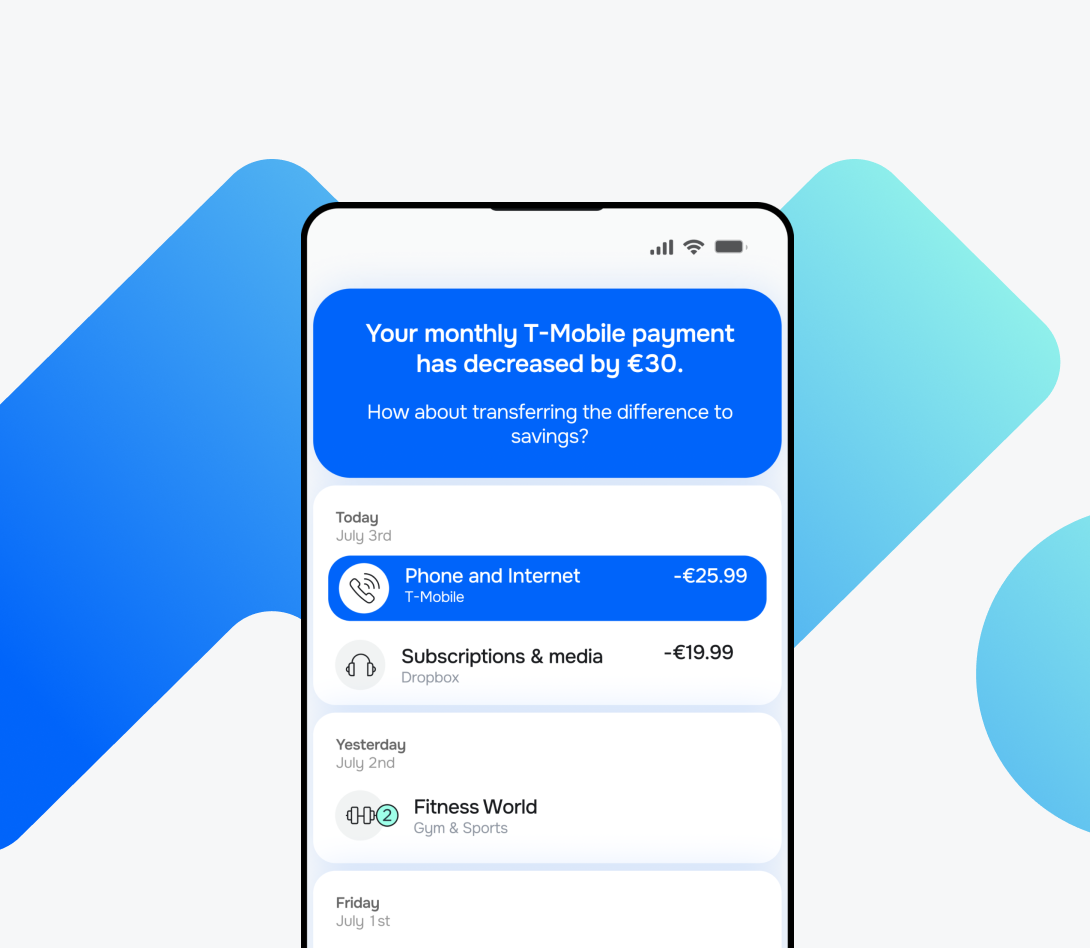
This level of adaptability builds trust but also strengthens customer loyalty through tangible financial support.
Moreover, smart savings tools can integrate seamlessly with behavioural nudges, gently prompting users to save a little more after a period of discretionary spending or celebrating milestones to reinforce positive habits.
The result is a personalised, frictionless savings experience that aligns with each customer’s financial rhythm.
By embedding AI-driven financial wellness features directly into digital banking platforms, banks can:
| Best practices for real-time personalised savings recommendations |
| Element | Description | Benefits |
| Progress visualisation | Visual tracking of savings goals through progress bars or percentage completion displays | Provides psychological motivation and continuous engagement |
| Reward systems | Digital badges, points, and cashback incentives awarded for saving or positive financial actions | Reinforces positive saving habits and creates an emotional connection with the app |
| Challenges and streaks | Gamified savings challenges and streak rewards for consistent saving or spending control | Boosts user commitment and long-term adherence |
| Social sharing and leaderboards | Community features that allow sharing goals, competing, or collaborating with peers | Introduces social accountability, increasing motivation and engagement |
| Automated AI-driven savings | AI adjusts savings contributions dynamically based on income and spending patterns | Ensures savings are manageable and adapted to user cash flow, facilitating sustainable habits |
| Real-time personalised nudges | Tailored recommendations and contextual nudges delivered based on user behaviour | Helps overcome impulse spending and maintain financial health |
Did you know?
Meniga enables banks to turn data into meaningful, personalised experiences.
Our platform delivers clear, actionable insights and recommendations tailored to each customer’s unique financial behaviour.
For example, when a customer gets a savings suggestion, the system explains why, linking it directly to their recent spending trends.
This transparency builds understanding and strengthens trust in the bank’s digital engagement.
How can you enhance the recurrent payment process with Meniga?
Meniga seamlessly integrates information from multiple internal systems, from credit cards and mortgages to investments, while also connecting to external data through open banking APIs.
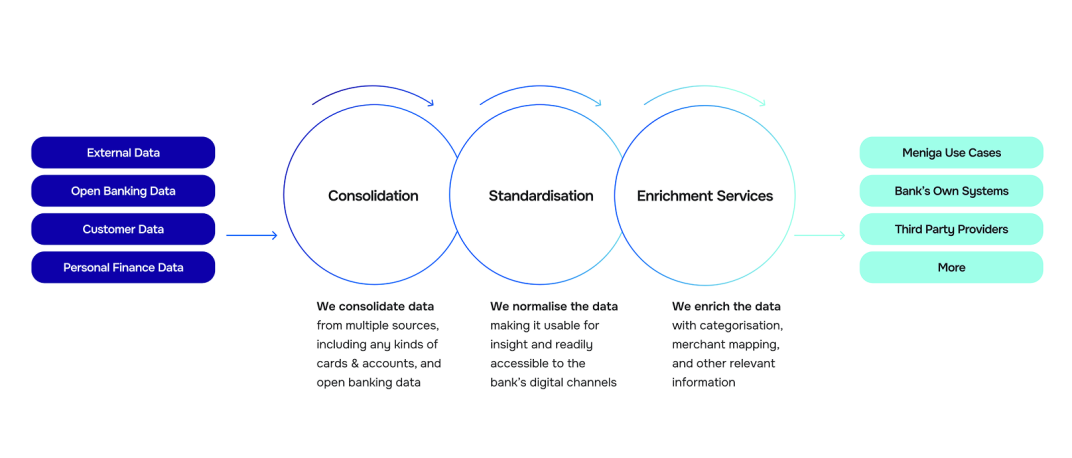
This consolidation eliminates data silos and provides a comprehensive view of customer activity across every financial product.
We enhance raw transaction data through precise categorisation of income and expenses and enrichment of merchant details.
Through AI-driven pattern detection, Meniga can detect recurring payments and upcoming transactions, ranging from subscriptions to utilities and mortgages, giving the end user a holistic view of their future spending.
Meniga turns fragmented data into actionable insights, giving banks a deeper understanding of their customers and enabling more relevant, personalised engagement.
With our solutions, you can move from reactive service to proactive financial engagement and:
-
Deliver personalised savings nudges and recommendations that guide customers toward better money management and smarter saving habits.
-
Trigger financial actions in real time, using insights from transaction patterns or external events to prompt timely saving opportunities.
-
Design hyper-personalised product offers and campaigns aligned precisely with each customer’s financial behaviour and needs, increasing conversion and revenue potential.
-
Notify customers of upcoming expenses or low balances, empowering them to stay in control and avoid financial stress.
-
Analyse behavioural data to build highly specific customer segments, such as 'Likely to Invest' or 'Starting a Family', enabling more relevant and effective engagement.
-
Ensure every message, offer, or recommendation reaches customers at exactly the right moment by leveraging real-life events.
Enticed to learn more?
Contact us today to see how you can start creating more personalised, data-driven banking experiences to drive stronger loyalty and sustainable growth.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between recurring and subscription payments?
Recurring payments are automatic transactions made at regular intervals, such as monthly loan repayments, utility bills, or insurance premiums, where the amount may vary each time.
Subscription payments, on the other hand, are a type of recurring payment tied to continuous access to a product or service, like streaming platforms or gym memberships, usually with a fixed fee.
All subscriptions involve recurring payments, but not all recurring payments are subscriptions.
2. What is a VRP in banking?
A Variable Recurring Payment (VRP) is an automated payment where the amount and frequency can vary each time, unlike fixed recurring payments.
VRPs allow customers to authorize a bank or payment provider to make multiple future payments to a merchant within agreed limits, offering flexibility for bills, subscriptions, or instalments.
VRPs give customers control over recurring transactions while enabling banks to support dynamic, automated payments securely and efficiently.
3. What are the 3 key AI techniques for optimizing recurring payments?
Three main AI techniques for optimizing recurring payments include:
-
Smart retry scheduling, which uses machine learning to determine the best timing and method for failed payment recovery.
-
Predictive analytics, which identifies customers at risk of payment failure or churn, enabling proactive interventions to maintain revenue and retention.
-
Personalised engagement that tailors communication, messaging, and alternative payment options to individual customer behaviours and preferences, often supported by AI-driven chatbots for continuous assistance.








