It is a fact that banks are navigating a vast amount of data, from real-time transactions to customer profiles, credit histories, and compliance records.
However, when you confuse transaction data with master data, the risks go beyond inefficiency.
It can trigger regulatory breaches, misinformed lending, and flawed AI-driven risk models.
If your bank makes decisions based on incomplete or misclassified data, our blog is a must-read.
Read on to learn the essential difference between transaction and master data, so that you can structure your data for scalability, compliance, and performance.
What is transaction data?
Transaction data is time-stamped records of individual business activities or events.
It captures what happened, when it happened, and who or what was involved, such as a payment, fund transfer, trade execution, or account login.
Key characteristics of transaction data:
-
Dynamic — Changes continuously as new transactions happen.
-
Event-specific — Each record details a specific event or exchange, such as a sale, a deposit, etc.
-
Volume — Generated in much larger quantities than master data.
-
Operational use — Primarily supports day-to-day business processes and real-time decision-making.
-
Short-term relevance — Often archived or summarised after its immediate use, unless it's aggregated for analytics or audit.
Examples of transaction data include payment confirmations, loan disbursements, card swipes, customer account updates, and other similar transactions.
However, transaction data only makes sense when tied to accurate master data.
Transaction data vs master data: What's the difference?
Simply put, transaction data describes the ‘verbs’ or activities within a business, such as sales, purchases, etc.
Conversely, master data describes the ‘nouns’ in your business, such as customers, products, suppliers, and locations.
However, the difference goes way beyond these two basic descriptions.
Here's a quick summary of the key differences between transaction and master data.
| Characteristic | Master data | Transaction data |
| Stability | Relatively constant over time | Continuously changing |
| Uniqueness | Represents unique entities (one per customer) | Records specific events (multiple per entity) |
| Consistency | Uniform across systems | Varies by event details |
| Cross-functionality | Used by many departments | Primarily operational, department-specific |
| Longevity | Long-term, historical reference | Short-term, often archived |
| Volume | Lower volume | High volume, frequent updates |
1. Stability
Transaction data is the live stream of everything your customer does: payments, transfers, deposits, withdrawals.
It’s constantly moving and always updating. Your system logs millions of events in real time.
Every time someone taps their card or sends money through your app, that action is instantly recorded.
And with AI-powered tools now monitoring these transactions as they happen, you can flag fraud, detect suspicious activity, or spot unusual behaviour within seconds.
Now, contrast that with master data, the more stable and foundational of the two.
It tells you who the customer is and what their relationship with you looks like.
Details such as their name, address, account number, KYC status, and account type rarely change, but they’re essential for understanding those real-time transactions.
For example, your customer, Sam Smith, transfers $10,000 from his savings account to his investment account.
What do the two different types of data tell you?
The transaction data captures: ‘Sam Smith transferred $10,000 on June 18, 2025, at 2:04 PM via mobile app.’
The master data stores: Sam Smith, age 40, verified identity, based in Munich, has a savings and an investment account, both in EUR, risk profile: moderate.
In addition, as AI evolves, banks are now enriching profiles with dynamic insights such as
So while master data doesn’t change every second, it’s no longer static either.
2. Uniqueness
Every transaction tells its own story, be it a wire transfer, an ATM withdrawal, or a loan payment.
Each one is unique, recorded with the exact time, amount, and details of the event.
And with (digital) banking platforms handling billions of these actions every year, the volume adds up fast.
On the other hand, master data is about the people and accounts behind those transactions.
It could be a customer profile or an account number, something that stays consistent and connects all those transactions.
To keep things accurate, banks use tools such as master data management (MDM) systems to make sure each customer or account is only represented once, even if they use multiple products or channels.
3. Consistency
Transaction data isn’t always clean or consistent. A payment made through a mobile app may look different from the same payment at a branch or ATM.
Different systems, different formats.
That’s where AI and automation step in, to standardise and clean this data on the fly so it’s accurate and ready for analytics, fraud checks, and compliance.
Master data, on the other hand, must be consistent everywhere.
Whether a customer calls support, uses online banking, or visits a branch, you need to see the same profile.
That’s why you should leverage strong data governance and quality tools to keep customer records clean, up-to-date, and reliable across every channel.
Besides efficiency, it’s crucial for compliance and delivering a personalised experience.
4. Cross-functionality
Transaction data keeps daily operations running. It powers functions such as payments, fraud detection, AML checks, and customer support.
Furthermore, AI uses this data to personalise marketing, flag risky behaviour, and spot trends across departments.
Master data is the backbone everyone relies on.
It is shared across all banking functions, retail, corporate, compliance, risk, and marketing, to provide a single source of truth.
This way, all teams pull from the same core customer and account data.
As a result, your bank can offer a smooth experience across channels and generate consistent, accurate reports.
5. Longevity
Transaction data is mostly used in real time to process payments, answer customer questions, or detect fraud. But it doesn't mean it disappears afterwards.
You archive it for audits, investigations, and long-term analysis.
With digital banking growing rapidly, storing all this data at scale means relying on cloud and AI to keep it organised and easy to access.
Conversely, you keep master data for the long term.
It’s the official record of who your customer is and how they’re connected to your products.
It changes slowly, but it’s essential for maintaining strong relationships and meeting regulatory requirements over time.
6. Volume
As we’ve already mentioned, the volume of transaction data is massive due to the adoption of digital banking, real-time payments, and increased customer interactions.
It’s a massive stream of data that requires AI and automation for monitoring and analysis.
Master data volume is comparatively smaller but just as important.
It includes millions of unique customer profiles, accounts, products, and relationships that underpin transactional data.
| Why real-time synchronisation of transactional and master data matters |
| Key reasons | Description |
| Immediacy and customer expectations | -
Customers expect real-time updates on transactions and changes. -
Syncing ensures that updates are instantly reflected in the profile, boosting trust and satisfaction. |
| Eliminating data fragmentation and duplication | -
Customer data is often stored in multiple systems. -
Real-time sync with MDM consolidates and cleans data, preventing duplicates and ensuring a single, reliable customer view. |
| Improved decision-making | -
Accurate, up-to-date data feeds better decisions. -
Real-time sync supports analytics, AI, and customer apps with the latest info for personalisation, risk scoring, and more. |
| Operational efficiency and SLA Compliance | |
| Consistent customer experience across channels | -
All teams can see the same data. -
This prevents miscommunication and duplicate outreach, improving omnichannel consistency. |
| Regulatory compliance and risk reduction | -
Accurate master data synced in real time helps meet data privacy, governance, and audit requirements, minimising compliance risk. |
Why must transaction data and master data work together?
Banks rely on the complementary nature of the two data types working together: transactional and master data.
Transaction data fuels the day-to-day, real-time payments, fraud detection, and customer activity. It’s fast, high-volume, and always changing.
Master data, on the other hand, is the anchor. It provides a stable, consistent foundation for identity, compliance, and customer experience.
When combined, they enable secure, efficient, and personalised banking.
To make it all work at scale, banks rely on AI, automation, and robust data governance, particularly as customer expectations rise and risks evolve.
Meniga acts as a bridge between the stable core of master data and the fast-moving flow of transactional data, helping you leverage the full value of your data assets to deliver smarter, more personalised customer experiences.
How to make transaction and master data work together with Meniga?
Meniga pulls together transactional data from your bank’s core systems or external sources, such as open banking APIs.
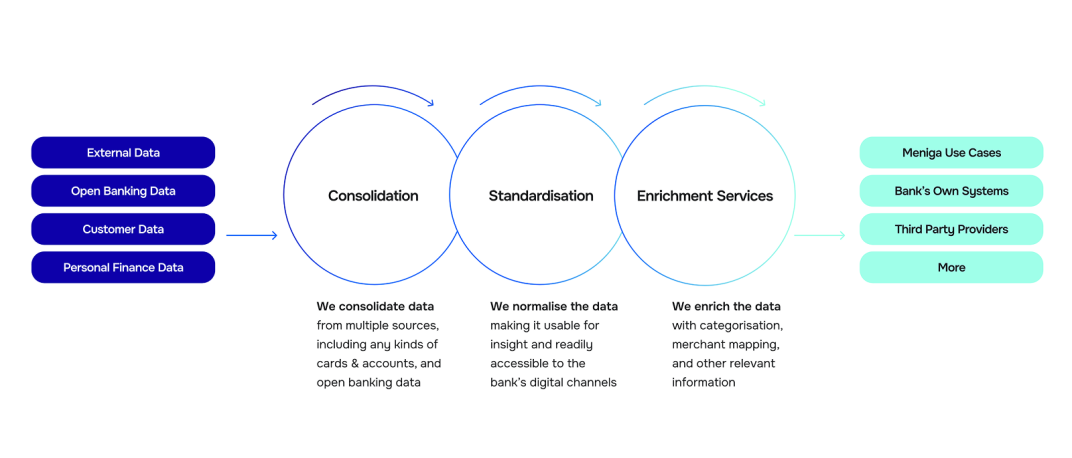
Once the data is in, our Enrichment engine gets to work.
It categorises and cleans the transactions, adding practical details that make the data easier to understand and more actionable, both for you and your customers.
Over time, the engine gets smarter by learning from user feedback and community patterns, improving its accuracy as it evolves.
As a result, transactions are clearer and more meaningful.
You get merchant names with logos, clean descriptions, recurring subscription detection, spending insights, and more, transforming raw data into actionable assets.

What else is in store for you?
-
Detect patterns, such as recurring payments or life events, thanks to machine learning, providing you with deeper insights into customer behaviour.
-
Access AI-Powered Hyper-Personalisation Platform — Build trust and loyalty through timely financial advice, like reminders for outstanding payments.
-
Increase engagement by encouraging customers to use existing digital tools, such as Cashflow Forecasting, for better financial planning.
-
Drive product adoption and digital sales with ultra-relevant, personalised recommendations at the moment customers need them, like offering short-term loans for unpaid expenses.
-
Track balance trends and use historical data to forecast future cash flow with our ML-powered Cashflow Forecasting.
-
Identify recurring income and expenses automatically.
-
Alert customers of potential overdrafts or missed payments in advance.
-
Automate savings and help customers stay on top of their finances, avoid late fees, set category-based budgets, get auto-suggestions based on income and expenses, and much more.
Enticed to learn more?
Contact us today to start turning raw customer data into real customer insight for better personalisation.


