Whenever customers use “Buy Now, Pay Later” at checkout or buy insurance through a ride-hailing app, they’re actually using banking products, often without realising it.
While the experience is smooth for users and profitable for banks, it limits the bank’s role to just the transaction, missing a valuable chance to build deeper engagement and lasting loyalty.
The competition isn’t just other banks anymore, but every brand embedding financial services into its customer journey.
But what is embedded finance, and how does it work?
Read on to learn about embedded finance to see how your bank can use this opportunity to extend its reach and create new revenue streams.
What is embedded finance?
Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services, such as banking, payments, lending, or insurance, directly within the services customers already use from non-financial companies.
The integration typically happens through APIs.
This approach enables customers to access financial solutions within the platforms they already use, eliminating the need to interact with traditional banks or separate financial institutions.
By delivering financial services at the point of need, embedded finance enhances the customer experience and opens new revenue opportunities.
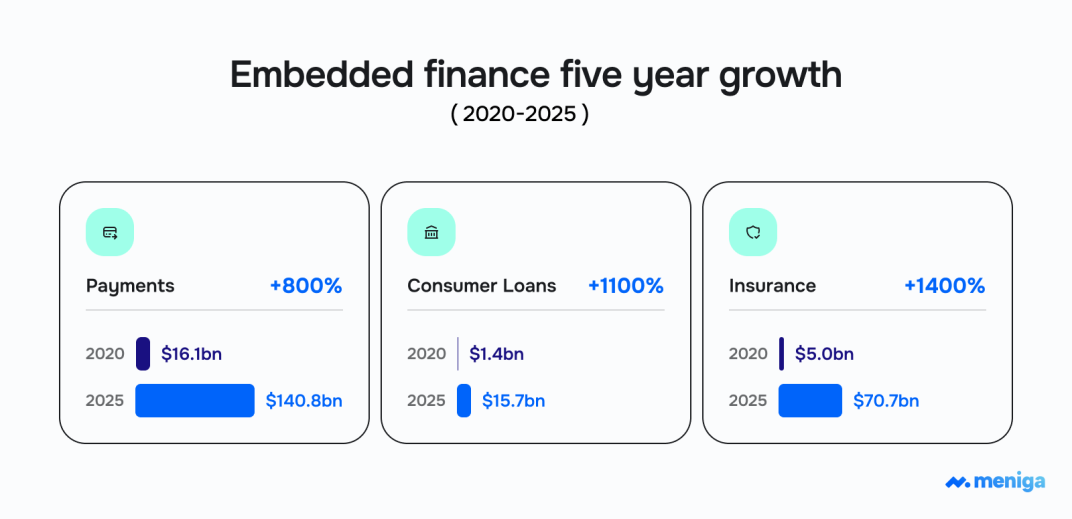
Source: Emarketer
How does embedded finance work?
A business, such as an e-commerce site, a ride-hailing app, or a SaaS platform, wants to offer financial services, such as payments, credit, or insurance, to improve customer experience and increase revenue.
However, most businesses aren’t banks, and they do not intend to become one.
Instead, they partner with banks that handle compliance, licensing, and financial infrastructure.
The financial service is integrated into the platform using APIs that enable seamless and secure connectivity between the financial provider and the business platform.
| Role of APIs in embedded finance | Description |
| Seamless integration | APIs enable secure, real-time communication between non-financial platforms and financial services, allowing financial functions like payments and lending to be embedded smoothly within apps without users leaving the platform. |
| Tailored financial products | APIs allow customisation and dynamic adaptation of financial services to meet specific customer needs contextually, enabling innovative products like instant loans or embedded insurance. |
| Driving innovation and efficiency | APIs reduce development complexity and costs by offering standardised connectivity, facilitating rapid deployment, operational efficiency, and continuous innovation in financial service offerings. |
Customers access financial services within the platform they already trust, without being redirected to a separate banking interface.
The embedded finance provider and the platform share revenue from the financial service, while the bank ensures compliance with KYC, AML, and other regulations.
What benefits does embedded finance bring to banks?
Embedded finance enables banks to expand their reach and revenue by integrating financial services into everyday customer interactions beyond traditional bank channels.
Let’s see what happens as a result.
1. Open new revenue streams
By partnering with embedded finance platforms, banks can access fresh sources of deposit and transaction-based income from both retail and commercial customers that otherwise might never walk into a branch.
Beyond traditional banking fees, banks benefit from being embedded in non-financial ecosystems, capturing value where customers are already engaged.
| Revenue stream aspect | Description |
| New partnership and platform revenue opportunities | Banks generate fees by partnering with fintechs, earning revenue from services embedded in non-bank platforms without having to handle all customer interactions. |
| Acceleration of fee-based and transactional revenue | -
Embedded finance increases financial activity volume by embedding services where customers interact, raising transaction frequency. -
Banks monetise growth via payment processing fees, lending margins, and insurance premiums, scaling beyond traditional customer bases. |
| Loss of visibility but opportunity for innovation | Embedded finance decreases banks’ brand visibility and direct customer links but incentivises banks to innovate digitally and adopt API-driven models, opening new revenue streams through |
| Growth in serving underserved segments | Embedded finance uses alternative transaction data to provide credit and financial services to underserved individuals and MSMEs, helping banks expand lending and fee income in new markets. |
2. Reduce customer acquisition costs
Acquiring customers through trusted third-party platforms significantly reduces the cost and complexity of direct acquisition.
Embedded finance enables banks to leverage existing customer bases, enhancing conversion rates and reducing marketing overhead.
3. Expand into new customer segments
Embedded finance provides an entry point into underserved or previously unreachable markets, including unbanked populations.
By integrating with widely used platforms, banks can scale their operations without relying on costly branch networks.
4. Accelerate go-to-market with cost efficiency
Instead of building solutions from scratch, banks can leverage API-driven embedded finance platforms to launch products faster, at lower development costs.
As a result, you can shorten innovation cycles and keep your bank competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
5. Strengthen customer loyalty and experience
When financial services are seamlessly integrated into platforms customers already trust, it creates a frictionless experience.
This convenience drives loyalty, builds trust, and meets a wide range of financial needs in a single, integrated environment.
How does embedded finance differ from traditional banking services?
Embedded finance differs from traditional banking services primarily in how and where financial services are offered, the customer experience, and the business model behind them.
Integration and customer experience
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce sites, ride-sharing apps, or SaaS products, allowing customers to access payments, lending, or insurance services without leaving the platform they are already using.
Traditional banking services, in contrast, require customers to interact with banks or financial institutions separately through their dedicated apps, websites, or physical branches.
Customer relationship and ownership
In embedded finance, the non-financial platform maintains the primary customer relationship and integrates financial services into the customer journey.
Traditional banks hold direct customer relationships and provide standalone financial products.
Regulatory and infrastructure
Traditional banks operate under their own banking licenses and handle all regulatory compliance themselves, offering comprehensive banking services.
Embedded finance companies typically partner with licensed financial institutions and use APIs to offer specific financial services within their ecosystem, sometimes taking on some regulatory responsibilities depending on the service offered.
Business model and market focus
Embedded finance focuses on enhancing the core business by embedding useful financial services to improve customer engagement, convenience, and monetisation. Traditional banking is centred on providing a broad array of financial products independently.
Embedded finance targets customers across various industries by combining financial and non-financial services, whereas traditional banking primarily serves consumers and businesses through financial channels.
What are the different types of embedded finance?
1. Embedded banking
Embedded banking integrates core banking services, such as accounts, debit or payment cards, fund management, and transaction tracking, directly into digital platforms.
As a result, financial management becomes much easier for customers.
Instead of opening separate bank accounts or logging into traditional banking apps, customers can access essential banking functions within the platform they already use.
This integration simplifies day-to-day financial operations, helping individuals and businesses:
For banks, embedded banking offers a way to extend their services into new customer touchpoints, build deeper engagement, and generate additional revenue streams without requiring customers to engage directly with traditional banking channels.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) and embedded banking: What’s the difference?
Although these two concepts are related, they do differ.
BaaS acts as the API-driven banking backbone, enabling 3rd parties to build comprehensive banking experiences.
On the other hand, embedded banking is the consumer-facing integration of banking features inside everyday non-financial apps and platforms.
| Aspect | Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) | Embedded Banking |
| Definition | Provides financial institutions' technological and regulatory infrastructure via APIs for 3rd-party companies to build banking products. | Deep integration of banking services directly into non-financial platforms or apps. |
| Purpose | Enables companies to offer full banking features, such as account creation, payments, lending, and compliance, without building infrastructure or holding licenses. | Embeds specific banking services contextually in platforms for seamless user transactions without leaving the app. |
| Scope of Services | Comprehensive, includes a full suite of banking functionalities: accounts, payments, lending, compliance, card issuing, and investments. | Focused on contextual banking services relevant to user activity, such as payments or loans, integrated directly in apps. |
| Target Users | Fintech companies, SMEs, and licensed 3rd parties seeking to offer banking products quickly with backend support. | General consumers using non-financial platforms |
| User Experience | Backend infrastructure is often invisible to the end-user. User interface provided by third-party companies. | Front-end integrated within a platform, enabling seamless transactions for users within their usual environment. |
| Regulatory Responsibility | BaaS providers handle regulatory compliance, licensing, and risk management. | The platform may rely on BaaS providers or banks for compliance. User-facing services are often masked as part of the platform. |
| Technology Use | API-based modular banking infrastructure enabling ‘banking à la carte’. | API integrations to embed financial services conveniently wherever needed in customer journeys. |
2. Embedded payments
Embedded payments integrate payment functionality directly into digital platforms, allowing customers to send, receive, and manage funds within the ecosystem.
It eliminates the need for separate banking apps or external payment processors, creating a smoother, faster, and more convenient financial experience.
With embedded payments, customers can access their funds instantly and make transactions in real time, whether for business operations, service fees, or personal expenses.
This flexibility allows customers to:
-
Manage cash flow efficiently,
-
Plan payments proactively, and
-
Reduce delays associated with traditional banking cycles.
For example, with a popular Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) option, you can embed instalment payment options at checkout across online retailers, letting customers spread payments without traditional credit checks.
For banks, embedded payments open opportunities to capture transaction fees and generate recurring revenue while strengthening engagement within partner platforms. By embedding payments into the tools and services customers already rely on, banks become an integral part of the digital ecosystem, offering convenience, improving financial agility, and enhancing customer loyalty.
3. Embedded lending
Embedded lending integrates financing directly into a platform, allowing customers to access credit or advance payments at the point of need.
Thus, customers don’t have to apply through traditional banking channels and can enjoy faster access to funds.
For customers, embedded lending improves cash flow by providing timely access to capital, whether for operational needs, purchases, or short-term expenses.
Customers can receive financing within the platforms they already trust, creating a seamless and intuitive experience.
For banks, embedded lending presents:
-
Opportunities to expand into new markets,
-
Generate interest income, and
-
Increase engagement without the overhead of traditional loan origination processes.
By leveraging platform data, banks can also assess risk more accurately and tailor lending solutions to the specific needs of customers.
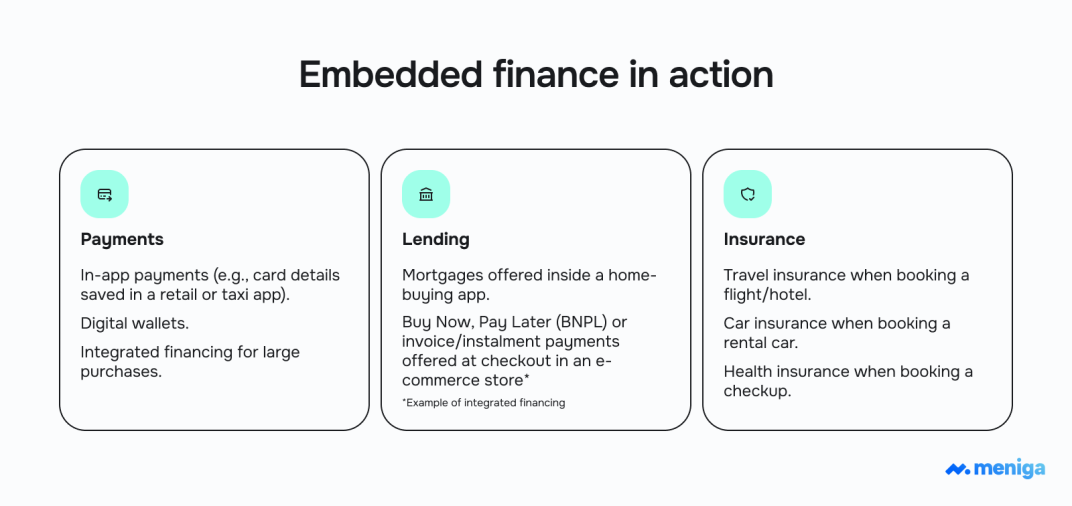
4. Embedded credit
Embedded credit allows customers, particularly small businesses or platform-based merchants, to obtain working capital or short-term credit directly within the tools they use daily.
Instead of seeking loans externally, users can manage their financing needs within a single ecosystem.
Besides simplifying cash flow management, this integration helps fund operations efficiently and reduces delays associated with conventional credit applications.
As a bank, you can benefit from precise credit risk assessment through platform data and strengthen your role as a trusted financial partner within digital ecosystems.
5. Embedded insurance
Embedded insurance lets customers get coverage directly while making a purchase or using a service, without dealing with separate providers.
Insurance products can be bundled with relevant offerings, providing coverage precisely when it’s needed.
For customers, this simplifies decision-making, improves efficiency, and enhances convenience by consolidating financial and non-financial transactions in one place.
For banks, embedded insurance expands distribution, increases engagement, and drives fee-based revenue, while embedding the institution more deeply into the customer’s financial journey.
6. B2B embedded finance
B2B embedded finance embeds financial services directly into the software and tools businesses use daily, such as:
By integrating financing options into these workflows, businesses can access loans, credit, and other financial products without leaving the platforms they rely on to run their operations.
These financial solutions are often tailored based on real-time data, including revenue streams, cash flow, and overall financial health.
Thus, businesses can receive credit limits, working capital advances, or payment solutions that fit their specific needs, reducing the time, paperwork, and friction typically associated with traditional financing.
For banks, B2B embedded finance opens opportunities to serve small and medium-sized enterprises more effectively.
By embedding lending, credit, or payment solutions into business platforms, banks can reach new market segments, generate fee and interest income, and strengthen long-term relationships.
At the same time, businesses benefit from faster access to capital, improved liquidity, and streamlined financial operations, all within the tools they already use.
How can you open new revenue streams through embedded finance with Meniga?
Meniga is a digital banking solution provider that combines data-driven insights and customer engagement tools to help banks and financial institutions deliver hyper-personalised and relevant products and offers.
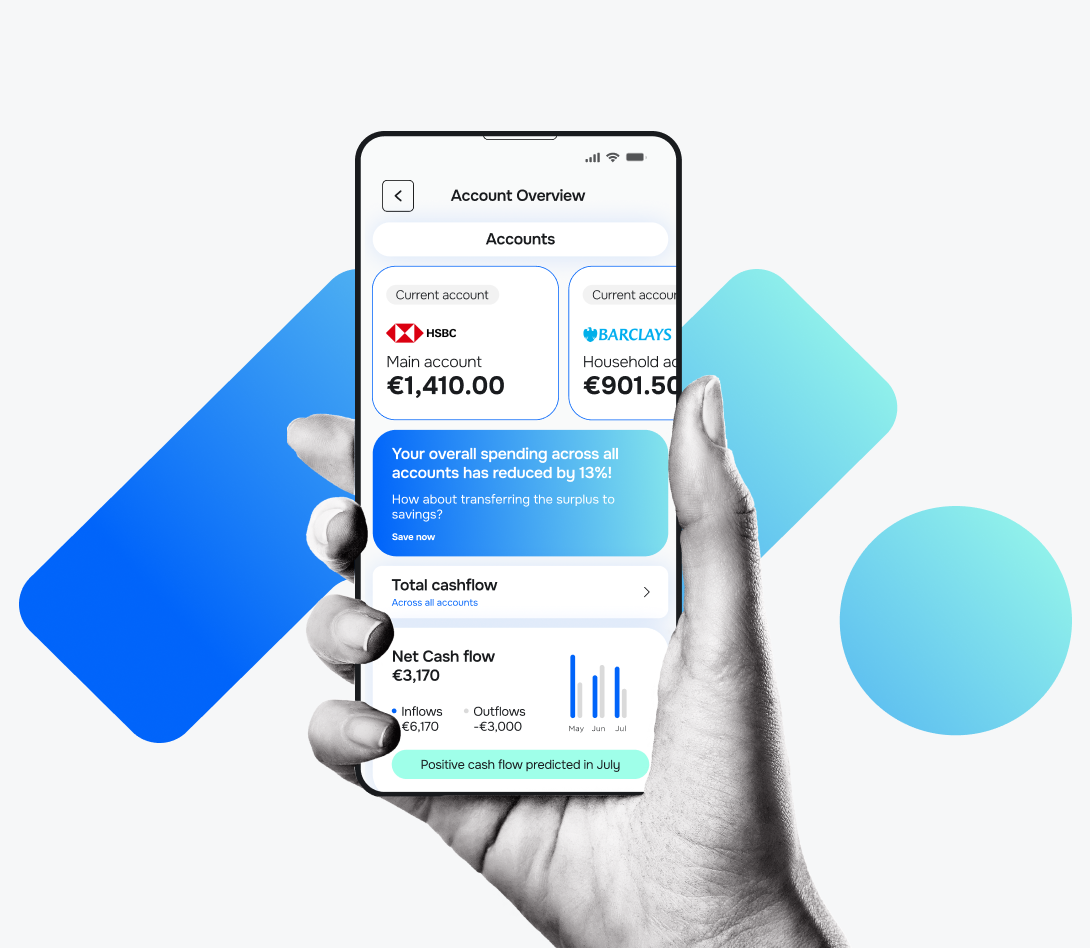
Here’s how you can leverage our solutions:
1. Maximise ROI on existing products: With our aggregated and consolidated customer transaction data and behaviour insights from internal and external sources, you can increase uptake and usage of current products such as credit cards, loans, and savings accounts.
2. Boost digital sales with targeted campaigns: Thanks to our advanced analytics and personalisation capabilities, you can run micro-targeted campaigns that promote embedded financial offerings to the right customers at the right time.
3. Capitalise on Open Banking: We leverage open banking APIs to enable seamless embedded finance experiences, expanding the scope of financial services you can offer directly within 3rd-party platforms, and thus increasing cross-sell and upsell revenue opportunities.
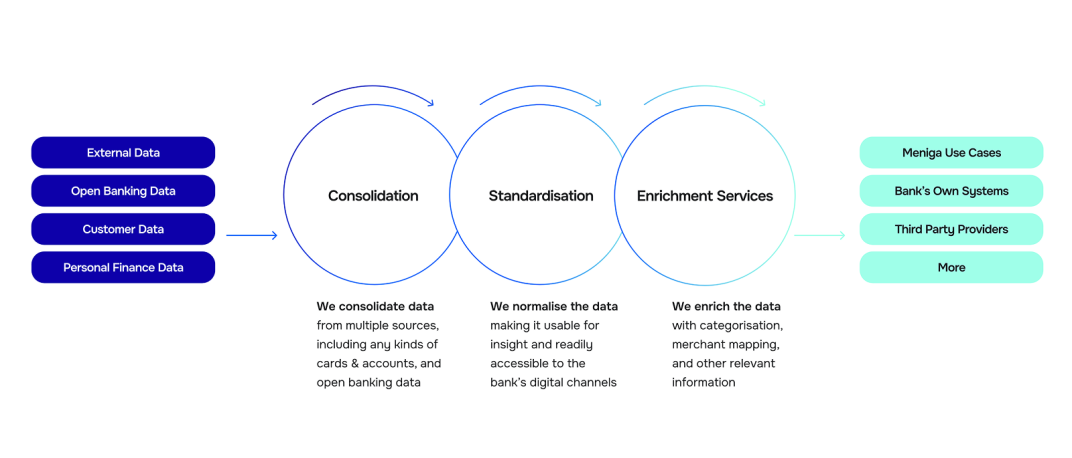
Our technology is highly flexible, allowing configuration to meet specific business logic and requirements. Data is processed in real time, normalised, and standardised, making it immediately accessible to the bank’s digital channels via Meniga’s RESTful API.
4. Enhance customer engagement and loyalty: Due to personalised insights and customer engagement tools, such as smart savings, you can increase loyalty and embed relevant financial products and services into everyday digital experiences.
Meniga’s solutions enable you to:
-
Create new revenue streams by hyper-personalising product offers.
-
Drive savings deposits to your bank with personalised insights or gamified savings linked to an external account.
-
Become the primary bank of choice by offering all financial data in your app and outperform competitors with superior offers.
Contact us today to see how you can strengthen digital engagement and develop new revenue streams through data-driven personalisation.








